- Our products
- Gokart
- Track consultation & Turn key project
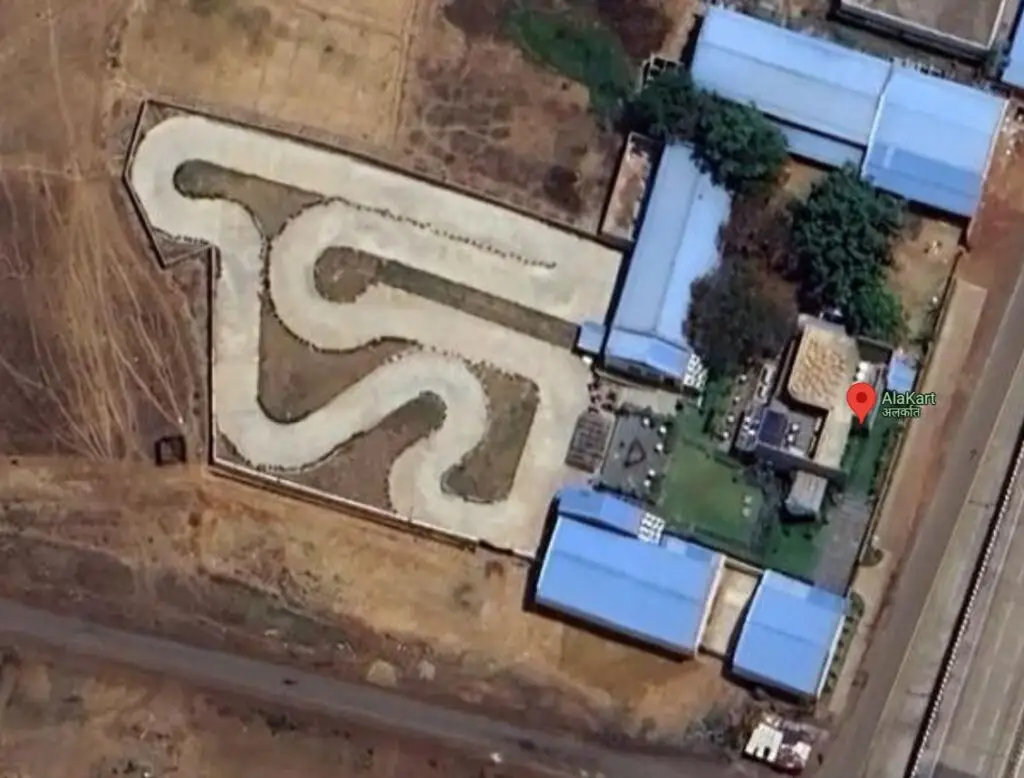
Track design & turnkey project
Designing a go-kart track for rental karting for business purpose, it is creative process that balances safety, excitement, and challenge for the karting drivers. The layout should take into account various factors such as space, track length, difficulty, and the flow of the course. Here are some essential elements and tips for designing a go-kart track as follow
Designing a go-kart track, it’s important to balance fun, safety, and excitement while making sure the layout is suitable for the types of karts you’ll be using. Here are key elements for a go-kart track design:


-
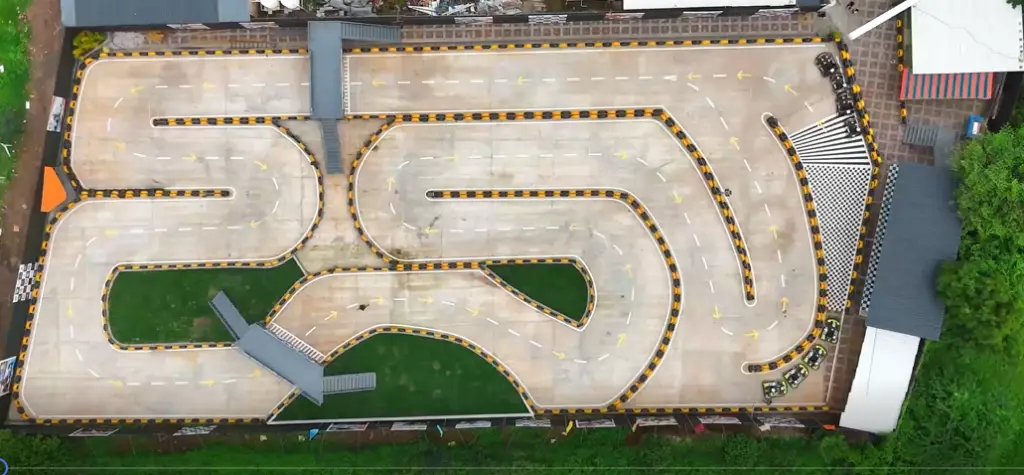
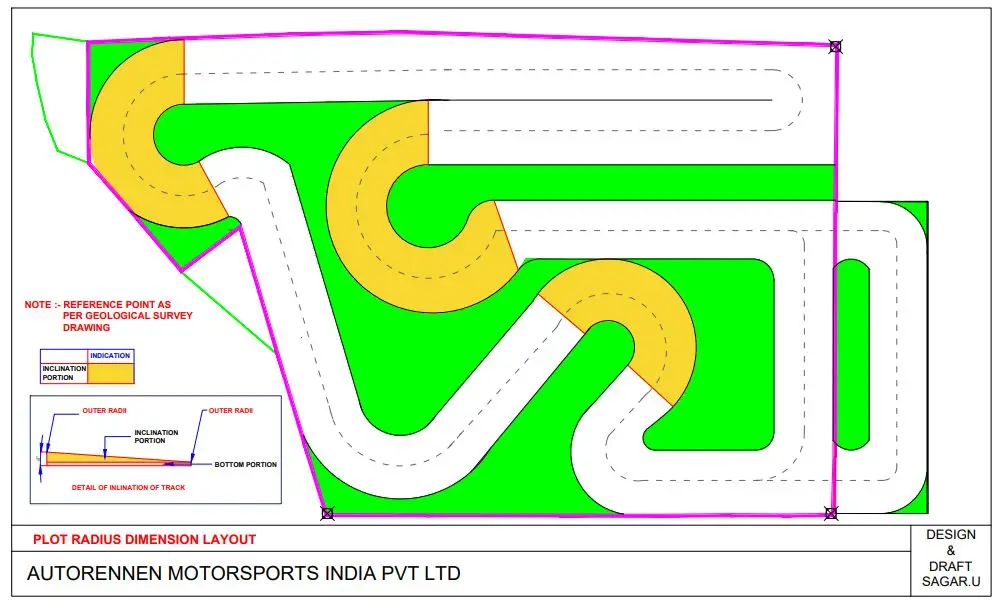
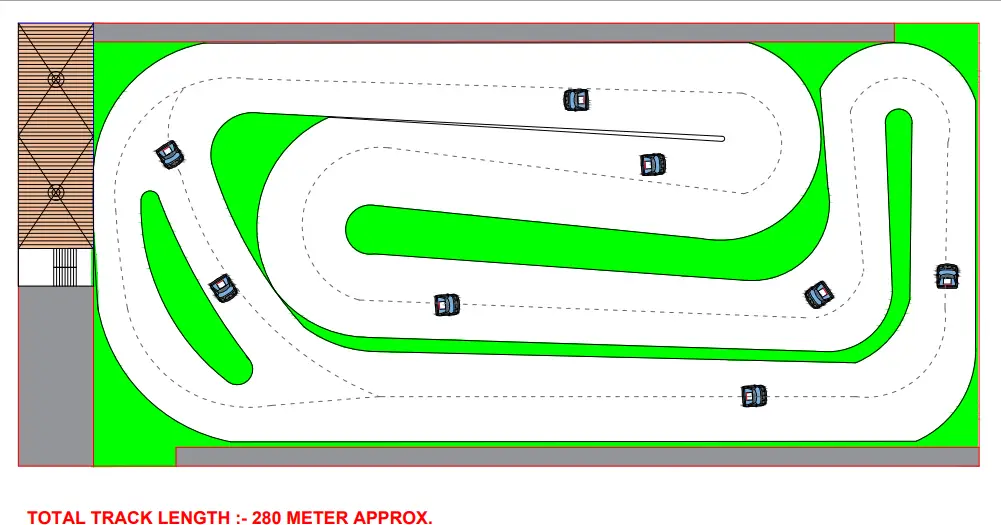
 Track Shape and Layout
Track Shape and Layout
-
 Safety Features
Safety Features
-
 Dimensions and Design Features
Dimensions and Design Features
-
 Pit Area
Pit Area
-
 Signage and Markings
Signage and Markings
-
 Environmental Considerations
Environmental Considerations
-
 Lighting (for Night Racing)
Lighting (for Night Racing)
-
 Additional Design Considerations
Additional Design Considerations
-
 Track Layout
Track Layout
-
 Track Layering
Track Layering
- Length: A typical recreational go-kart track is between 1,000 to 1,500 feet long (300 to 450 meters).
- Corners: Include a mix of tight corners and wide turns. Sharp corners will slow down karts, while long, sweeping bends can allow for higher speeds.
- Elevation Changes: Slight inclines or declines can add excitement, but avoid steep hills that could cause safety issues or high-speed crashes.
- Straights: Include long, straight sections for the karts to reach top speed.
- Barriers: Use sturdy, cushioned barriers (such as plastic barriers or foam padding) along the track to absorb impacts and reduce injury risk.
- Run-off Areas: Leave enough space around the track for karts to safely exit without crashing into barriers.
- Corners Design: Curves should be designed to help reduce the risk of oversteering. Banked corners can help with this, although they must be gentle and gradual.
- Track Surface: Ensure a smooth, durable surface (asphalt, concrete, or specialized track surface) that provides sufficient grip.
- Track Width: A minimum of 8-10 feet is ideal for kart racing. This allows enough space for cars to maneuver without being too tight.
- Turning Radius: For safe turns, a larger radius is better, especially for high-speed sections.
- Viewing Areas: Designate viewing zones for spectators, such as raised platforms or bleachers along the side of the track.
- Pit Lane: For racers to exit and enter the track safely. This should be wide enough for drivers to enter or exit quickly.
- Pit Stop: Have a designated area for go-kart maintenance, refueling, and repairs.
- Track Indicators: Clear markers showing corners, starting lines, and track boundaries help with orientation and safety.
- Speed Limits: Clearly displayed speed limits for specific areas (like chicanes or sharp turns).
- Track Direction: Indicate the flow of the track (counterclockwise or clockwise).
- Noise Control: Design the track layout and barriers to help contain sound, especially in residential areas.
- Weather: Plan for drainage to prevent flooding, and consider adding water-resistant track materials for rain.
- If your track operates after dark, incorporate adequate lighting. LED track lights help illuminate corners, straightaways, and the pit area.
- Start/Finish Line: Mark a clear starting and finishing line with appropriate signage and timing systems.
- Chicanes: Small sections of the track with sharp turns to slow down karts while increasing technical difficulty.
- Design for Multiple Layouts: Consider making the track modular so that different configurations can be used for different events or skill levels.
A. Beginner/Intermediate Track
- Length: ~400-600 meters.
- Features: 3 straightaways, 4-6 turns, one tight hairpin turn, a couple of moderate curves.
- Width: 10-12 feet.
- Speed: Moderate, with tight sections to encourage more technical driving.
B. Advanced Track
- Length: 800-1000 meters.
- Features: 5 straightaways, multiple sharp curves, an elevation change, long corners, and a chicane.
- Width: 12-15 feet to accommodate high speeds and multiple karts.
- Speed: High-speed zones with challenging tight corners for experienced drivers.
Go-kart track layering refers to the different layers of material and surface treatment used to create a safe, smooth, and durable surface for racing. Proper layering ensures that the track provides the necessary grip, durability, and safety, while also contributing to the aesthetic appeal.
Here are the key layers involved in go-kart track layering:
- Base Layer (Subgrade/Foundation)
- Drainage Layer
- Sub-Base (Compacted Base Material)
- Track Surface Layer (Top Layer Concrete/ Asphalt)
- Grip/Traction Layer (Surface Treatment)




